Categories
New Blog
Tags
Behind every pill you take lies a complex manufacturing process driven by tablet presses. These machines transform powders into tablets but can face various challenges that impact efficiency and quality. In this post, we'll uncover the top issues and offer practical solutions. Let's dive in!
A tablet press is a machine designed to compress powder or granular materials into compact, uniform tablets of a specific shape, size, and weight. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to manufacture medication tablets, as well as in the production of nutritional supplements, vitamins, confectionery, and various other solid dosage forms. The process involves feeding the material into the die cavity of the press, where it is compressed under high pressure to form a tablet, which is then ejected for further processing or packaging.
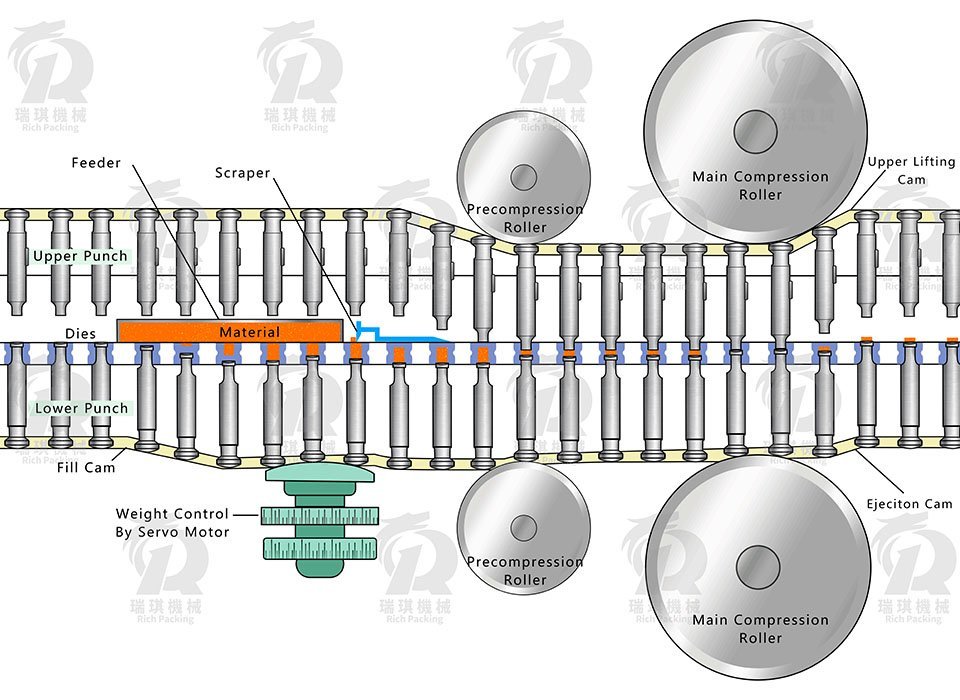
Punches and Dies: The powder is pressed under a mold by high pressure to make tablets of different sizes and shapes.
Feeding Mechanism: Ensure that the powder material is evenly filled into the mold through the feeding mechanism..
Compression Rollers: The powder is prepressed and then formed into a tablet under high pressure.
Ejection Mechanism: Releases tablets from the dies.
Now, let's understand the common problems of the tablet press in the production process and how to deal with it.
1. Compression Issues: The Pressure Problem
Problem: Compression is vital for tablet formation. Over-compression causes brittle tablets that crumble easily, while under-compression results in weak tablets that may disintegrate prematurely.
Solution:
Regular Calibration: Ensure the tablet press is calibrated regularly to maintain consistent compression forces.
Material Testing: Test the compressibility of the powder mix to determine the optimal pressure settings.
Adjustable Rollers: Use adjustable compression rollers to fine-tune the pressure applied during the compression cycle.
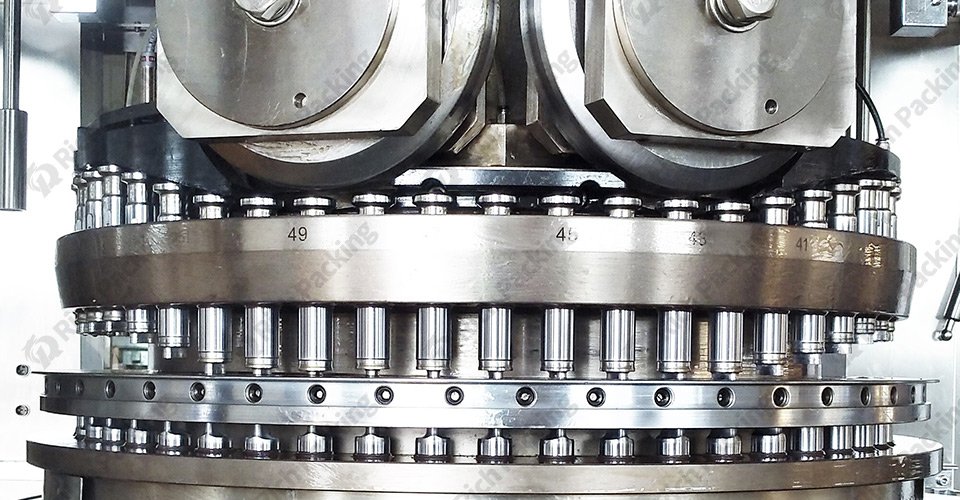

Problem: Malfunctions in the feeding mechanism can lead to uneven powder distribution, causing inconsistent tablet weights and thicknesses.
Solution:
Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections to check for wear and tear in the feeding mechanism.
Alignment Check: Ensure the feeder is properly aligned to prevent material spillage and uneven distribution.
Cleaning: Often clean the feed mechanism of the tablet press to ensure that each production cycle is cleaned once, so as to effectively avoid residue accumulation interfering with the uniformity of the powder.
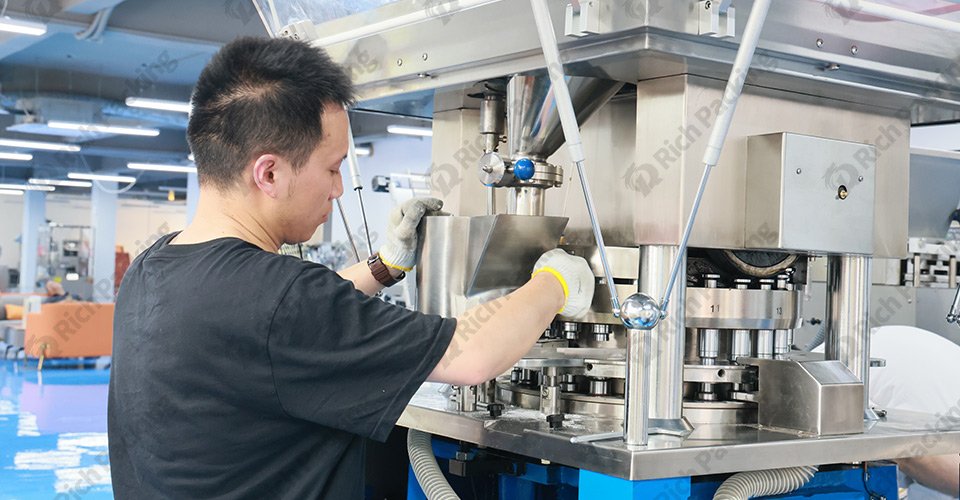

Problem: Over time, the dies used in tablet presses can wear down, affecting the shape and quality of the tablets produced.
Solution:
High-Quality Dies: According to the needs of finished products and raw materials, select high-quality and durable molds with appropriate materials.
Regular Replacement: Replace worn dies promptly to maintain tablet quality.
Maintenance Schedule: Develop a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of dies for signs of wear.
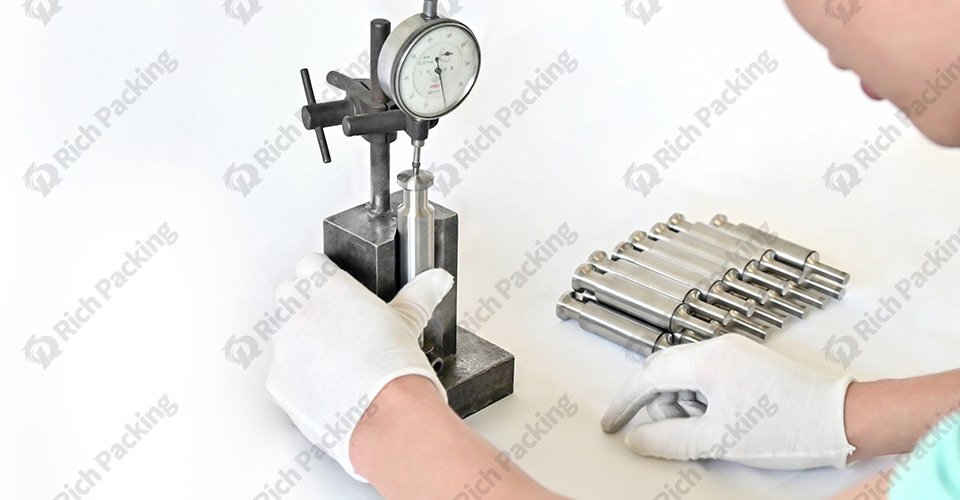

Problem: Poor die design or insufficient lubrication can cause ejection issues, leading to broken or misshapen tablets.
Solution:
Die Design: Opt for well-designed dies that facilitate smooth ejection.
Lubrication: Improve mold surface accuracy to reduce friction and prevent material adhesion.
Adjustment: Fine-tune the ejection mechanism to ensure tablets are released without damage.
Problem: Misaligned punches can cause issues such as chipping or cracking of the tablets during the compression process.
Solution:
Alignment Tools: Use precision alignment tools to ensure punches are correctly positioned.
Regular Checks: Conduct regular checks to confirm punch alignment remains accurate.
Replacement: Replace damaged punches to prevent misalignment-related issues.
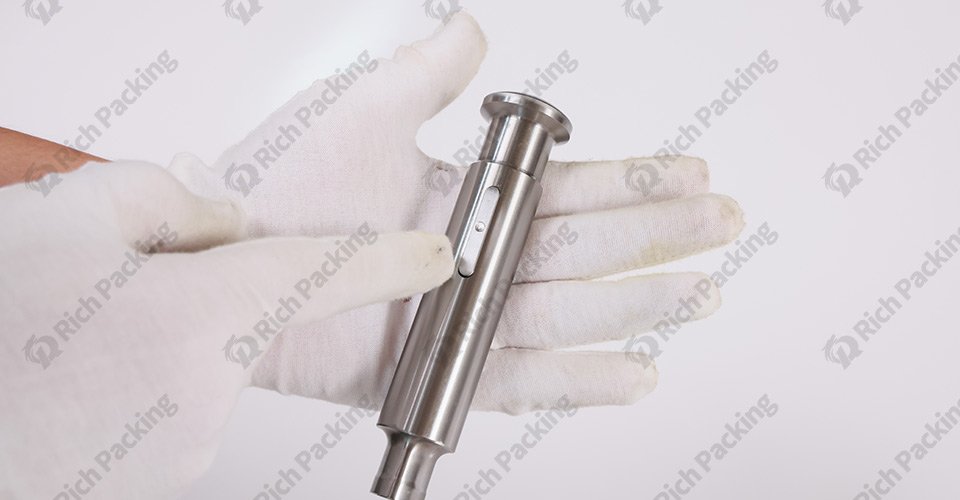

Problem: Adhesion occurs when the powder sticks to the punch faces, causing the tablets to have a rough surface or deform.
Solution:
Lubricant Selection: Choose the right lubricant based on the powder properties and the specific needs of the tablet press.
Application Method: Use an appropriate application method (spray, brush, etc.) to ensure even coating.
Moisture Control: Control the temperature and humidity of the production environment to prevent the powder from absorbing water and preventing adhesion.
Problem: Neglecting cleaning and maintenance can lead to buildup of residues, contaminating future batches and affecting tablet quality.
Solution:
Cleaning Protocols: Establish strict cleaning protocols to prevent cross-contamination between batches.
Scheduled Maintenance: Set up a maintenance schedule that includes regular cleaning and inspection of all components.
Operator Training: Train operators on the importance of proper cleaning and maintenance practices.
Problem: Issues like tablet weight variability, hardness inconsistencies, and disintegration time deviations can compromise the efficacy and safety of the final product.
Solution:
Automated Testing: Implement automated testing systems to monitor and adjust tablet characteristics in real-time.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Use SPC methods to track production data and identify trends that could indicate quality issues.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with regulatory standards for quality control and documentation.
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of your tablet press components to identify wear and tear early on.
Calibration: Regularly calibrate the compression force to ensure consistent tablet hardness.
Skill Enhancement: Organize regular workshops to update operators' knowledge. Encourage peer-to-peer learning and cross-training.
Maintenance: Select appropriate lubricants for equipment needs. Implement a detailed lubrication schedule. Regularly assess lubricant performance and adjust as needed.
Cleaning Protocols: Establish strict cleaning protocols to prevent cross-contamination between batches.
Through reading the above content, I believe that you have a comprehensive understanding of the common problems encountered in the production of the tablet press, and only need to deal with the corresponding problem according to the solution, you can ensure that the quality of the product is improved in the production process and meets the production standards of high-quality finished products. Regular maintenance, proper training, and effective troubleshooting are key to keeping your tablet press running smoothly. Stay tuned for our next post, where we delve deeper into advanced solutions and best practices for optimizing tablet press operations.